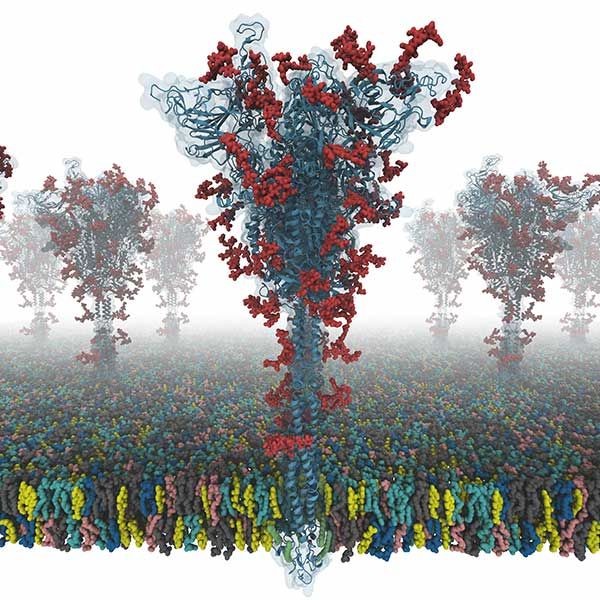
The virus SARS coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the known cause of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The “spike” or S protein facilitates viral entry into host cells.
Now a group of researchers from Lehigh University, Seoul National University in South Korea, and the University of Cambridge in the UK have worked together to produce the first open-source all-atom models of a full-length S protein. The researchers say this is of particular importance because the S protein plays a central role in viral entry into cells, making it a main target for vaccine and antiviral drug development.
This video illustrates how to build the membrane system from their SARS-CoV-2 S protein models. The model-building program is open access and can be found from the home page of CHARMM-GUI by clicking on the COVID-19 Archive link, or by clicking the archive link in the header, then the COVID-19 Proteins link in the left sidebar.
Developed by Wonpil Im, a professor in Lehigh’s Department of Bioengineering and the Department of Biological Sciences in the College of Arts and Sciences, CHARMM-GUI (GUI = graphical user interface) is a program that simulates complex biomolecular systems simply, precisely and quickly. Im describes it as a “computational microscope” that enables scientists to understand molecular-level interactions that cannot be observed any other way. More information about CHARMM-GUI can be found in this video.
“Our models are the first fully-glycosylated full-length SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein models that are available to other scientists,” says Im. “I was fortunate to collaborate with Dr. Chaok Seok from Seoul National University in Korea and Dr. Tristan Croll from University of Cambridge in the U.K. Our team spent days and nights to build these models very carefully from the known cryo-EM structure portions. Modeling was very challenging because there were many regions where simple modeling failed to provide high-quality models.”
Scientists can use the models to conduct innovative and novel simulation research for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, according to Im.
Read the full story in the Lehigh University News Center.
Story by Lori Friedman